Vapi Industries: Smoke vs. Heat vs. Flame Sensors
April 17, 2025
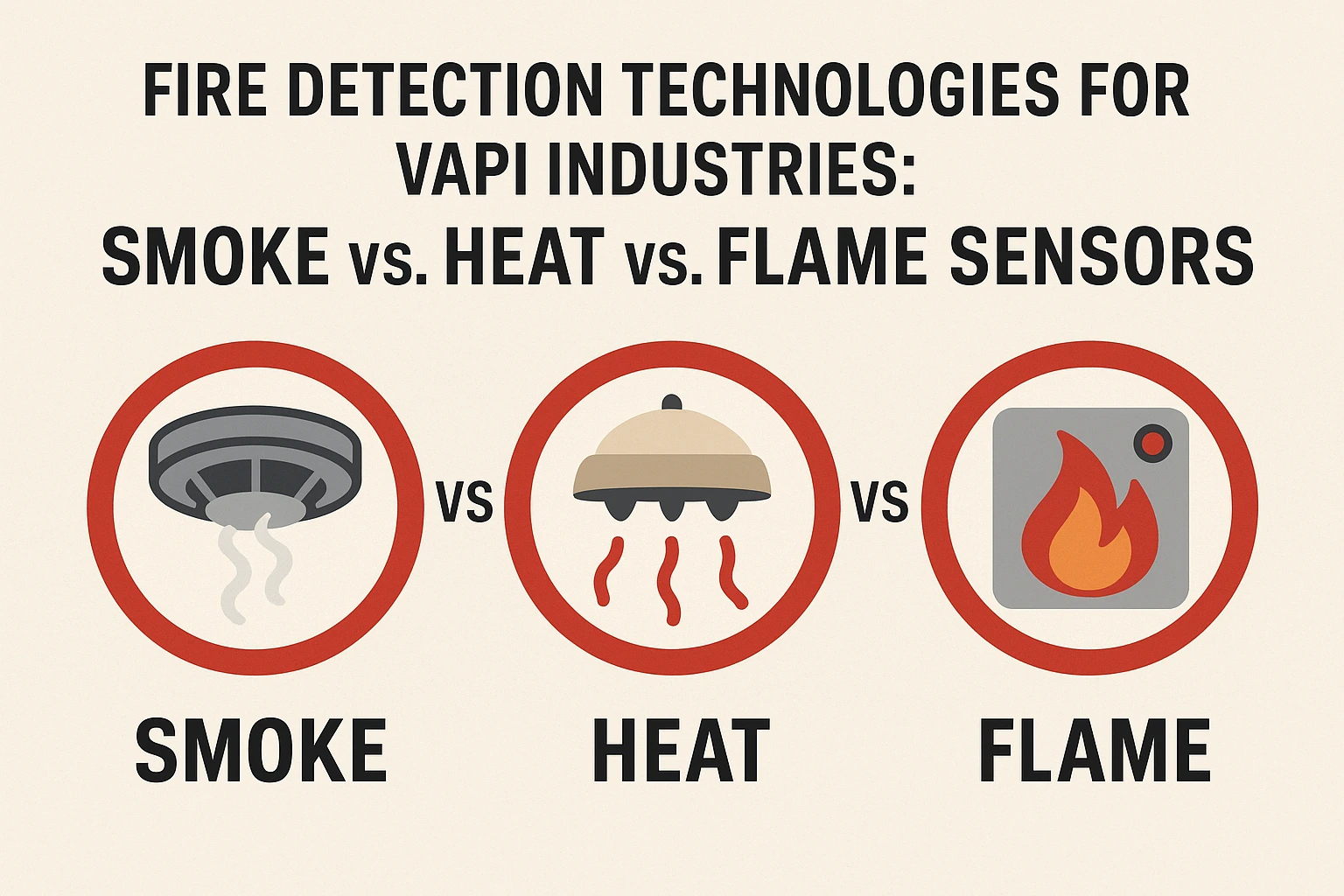
Table of Contents
Explore smoke, heat, and flame detection systems tailored for Vapi’s industrial environment. Learn their strengths, limitations, and how to choose, install, and maintain the right fire‐detection solution for your facility.
Introduction
In any industrial setting, early fire detection is the linchpin of a comprehensive safety strategy. In Vapi—home to chemical plants, textile mills, and warehousing hubs—choosing the right sensor can mean the difference between a minor incident and a devastating loss. This post compares smoke, heat, and flame sensors, helping you select the optimal solution for your local conditions.
1. Why Fire Detection Matters in Vapi Industries
Rapid Response: Vapi’s high‑risk zones (GIDC chemical estates, storage yards) demand sensors that detect threats before flames spread.
Regulatory Compliance: Gujarat Fire Safety Rules mandate automatic detection in key industrial areas.
Integrated Safety: Detection systems feed alarms, sprinklers, and control panels—an interconnected network that halts fire in its tracks.
2. Smoke Sensors
How They Work: Detect airborne particles from smoldering fires.
Pros:
- Very early warning—before heat or flame.
- Ideal for offices, control rooms, and enclosed spaces.
Cons: - Prone to false alarms in dusty or humid (monsoon) conditions.
- Not effective against fast‑flash fires with minimal smoke.
3. Heat Sensors
Types:
- Fixed‑Temperature: Triggers at a set threshold (e.g., 57 °C).
- Rate‑of‑Rise: Alerts on sudden temperature spikes (e.g., +8 °C/minute).
Pros: - Reliable in dusty, oily, or high‑humidity zones.
- Minimal false alarms from non‑smoke sources.
Cons: - Slower than smoke detectors—fires must generate significant heat.
- Less suited for early‑stage smoldering fires.
4. Flame Sensors
Variants: Infrared (IR), Ultraviolet (UV), or combined UV/IR detectors.
Pros:
- Instant detection of open flames—even over long distances.
- Effective in harsh outdoor or heavy‑machinery areas.
Cons: - Cannot detect smoldering fires without visible flame.
- Higher cost and more complex installation.
5. Choosing the Right System for Your Vapi Facility
Environment:
- Enclosed, air‑conditioned areas → Smoke sensors
- Dusty or oily workshops → Heat detectors
- Outdoor storage or high‑voltage zones → Flame sensors
Risk Profile:
- Smoldering risks (cable trays, paper storage) → Smoke
- Rapid‑flame risks (solvent handling) → Flame & heat
Budget & Integration:
- Combine sensor types to balance cost and coverage
- Ensure compatibility with your control panel or building management system
6. Installation & Maintenance Best Practices
Placement: Follow manufacturer spacing rules—typically one detector per 50 m².
Wiring & Power: Use fire‑rated cables and backup power (UPS or battery).
Testing: Monthly functional tests; full calibration annually.
Cleaning: Dust and insect screens reduce false alarms—schedule quarterly.
Record‑Keeping: Log all tests and repairs to satisfy Gujarat Fire Department audits.
7. Local Service & Compliance in Vapi
At Munshi Fire Safety, we offer:
- Site Surveys across Vapi, Valsad, Pardi, Dharampur & Umargam
- Custom System Design for GIDC plants and warehousing yards
- Certified Installation & Commissioning per IS 2189 and NFPA standards
- AMC Contracts to keep your sensors in top condition year‑round
Conclusion & Next Steps
Selecting the right fire‑detection technology is a matter of matching sensor capabilities to your facility’s unique hazards and environment. By integrating smoke, heat, and flame detectors where they excel—and maintaining them diligently—you build an interconnected safety net that protects lives, assets, and business continuity.
📞 Contact us today for a free site assessment and tailored proposal for “Fire Detection in Vapi Industries.”
commonly asked questions
What is the difference between smoke, heat, and flame detectors?
Smoke detectors sense airborne particles from smoldering fires. Heat detectors respond to high or rapidly rising temperatures. Flame detectors identify light emitted from open flames using UV or IR sensors.
Which sensor is best for a dusty warehouse?
Heat detectors are ideal for dusty environments. They are less prone to false alarms compared to smoke sensors in such conditions.
Can I use multiple sensor types together?
Yes, hybrid systems combining smoke, heat, and flame detectors provide layered protection. Integration with a central panel ensures cohesive response.
How often should sensors be tested?
Perform monthly functional tests and annual calibration. Clean them quarterly and log all maintenance for compliance.
Are flame detectors suitable for indoor use?
They can be used indoors but are most effective in open areas with a high risk of visible flames, like fuel-handling zones or machine yards.
What certifications should fire detection systems comply with?
In India, systems should comply with IS 2189. For international standards, NFPA compliance is also recommended.
Admin
Fire Safety Expert
Stay Updated
Get the latest fire safety tips and news delivered to your inbox.
Related Articles
No related articles found.